Abstract vs. Introduction: What is the actual difference?

If you’ve never written a research paper, the number of boxes to check to complete it can be intimidating. Even if it’s not your first rodeo, there’s still so much to think about that it’s easy to get confused.
The difference between an abstract and an introduction is a common concern for first-time research writers.
While these parts may seem similar at first glance, they have distinct characteristics. Whether you’re writing a paper to submit to a journal, an academic conference, or for your MSc or PhD, crafting a good abstract and a unique introduction will save you hassle in the revision stages and increase the likelihood of your paper being accepted.
What is the Difference Between an Abstract and an Introduction?
In around 250 words, an abstract summarizes the entire study and generates reader interest in your paper. An introduction is the first section of your paper. It covers background information, sets the context for your research, and is longer than an abstract (500 words or more).
The key difference between an abstract and an introduction is their purpose:
- An abstract is an advertisement.
- An introduction is a hook.
If you think of an abstract as an advertisement, it should be brief and summarize your paper entirely. People will have to spend their time (maybe even their money) reading your paper. So, your abstract should give them an initial idea of why your paper is relevant to them and what they can expect to learn.
Alternatively, thinking of your introduction as a “hook” means it’s the key to holding the long-term attention of a reader (once they’ve chosen to read your paper). An introduction isn’t about giving all of the research details, it’s about setting the scene for why the details matter.
Beyond purpose, the table below outlines the differences between abstracts and introductions:
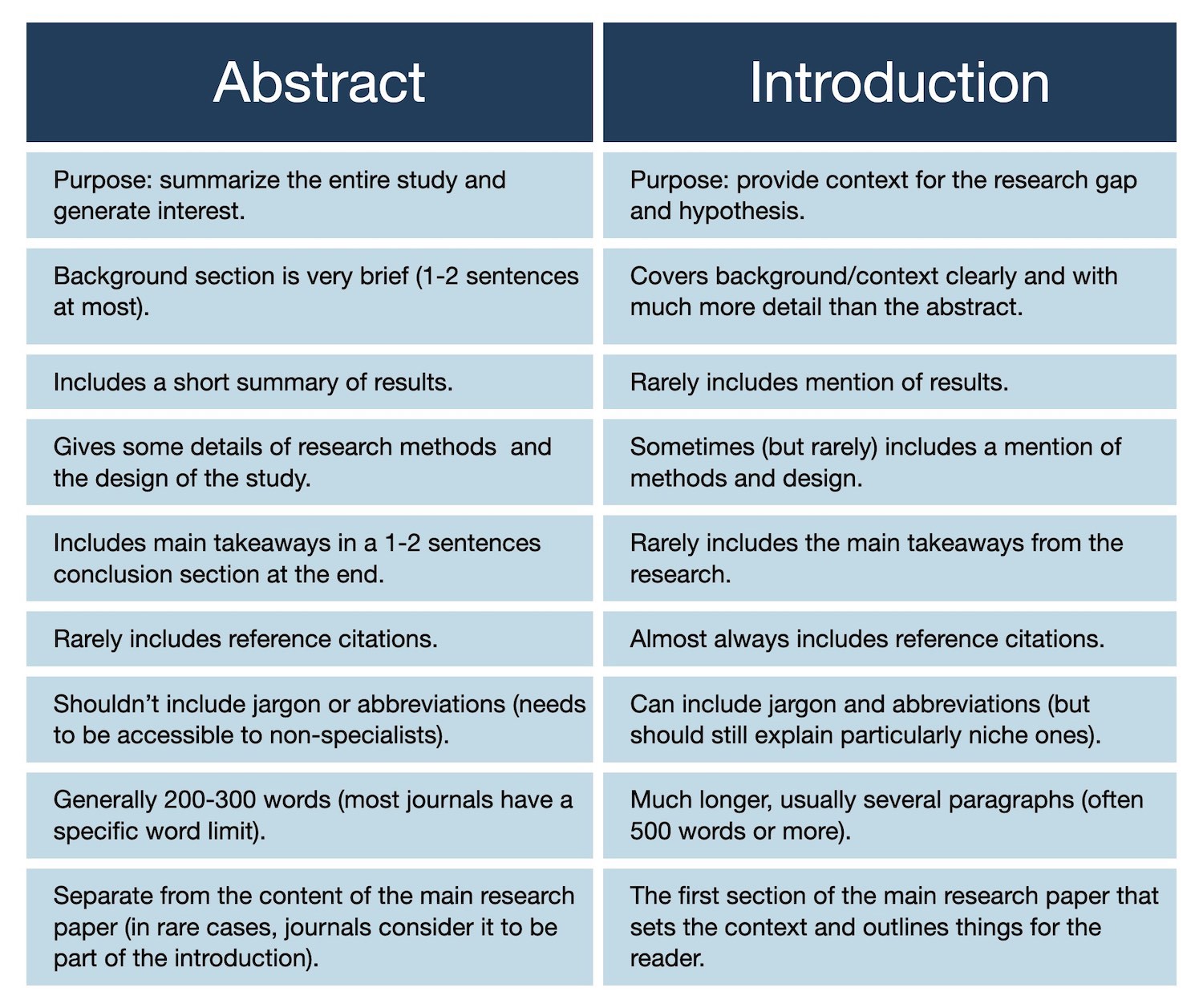
Comparison table showing the key differences between an abstract and an introduction.
How to Write a Good Abstract
Your abstract is likely the first thing people will read. It’s a particularly important tool for researchers that have to sort through piles of potential papers to review.
So, make it clear what your paper is about, why that topic is important, and what you found in your research. Here are 3 tips for writing a good abstract…
1. Consider your abstract format
There are two basic formats for abstracts. Often, the journal or program you are submitting to will outline what style they expect:
- A structured abstract includes section headings.
- An unstructured abstract is a single block of text.
Regardless of this structural difference, both of these formats focus on answering the same set of key questions for prospective readers:
- Context/Background: Why is this topic and this research important?
- Objective: What questions are you trying to answer in your research?
- Methods/Design: What are the basic details of your research? In general, how did you go about answering the research questions?
- Results: What answers did you find? Were there any other observations?
- Conclusion/Takeaways: Were your results expected? Is more research needed?
2. Keep your abstract clear and concise
Your abstract should efficiently deliver information in a way that non-specialists can understand. Detailed descriptions and scientific slang terms don’t belong here. Also, check specific author guidelines to know if there’s a word limit for your abstract (250 words is a common limit).
3. Beat writer’s block by outlining your paper
Just because your abstract is the first thing people will read doesn’t mean it’s the first thing you have to write. It’s helpful to have an outline or loose draft of your entire paper before you write your abstract. Highlight the most important points in each section, then use them to help frame your abstract.
How to Write a Good Introduction
After people have decided to read your paper, it’s your introduction’s time to shine. A good introduction sets the tone for the reader.
So, make sure that your introduction gives context to your research and makes it clear why your reader should care. Here are 3 tips for writing a great introduction…
1. Answer these questions in your introduction
Some content in your introduction may overlap with your abstract. But, your introduction should cover key questions slightly differently (and in more detail) than your abstract:
- Why is your field of research important?
- What background information is needed to understand your research (include references where applicable)?
- What earlier research impacts the context of your own or helps with understanding your research process?
- How is your research innovative or original?
- What are the sections included in the rest of the paper?
2. Don’t save your introduction for last
“Save your intro for last” is a common tip for various writing applications. But it doesn’t need to be a rule. As Rachael Cayley outlines in this blog post: “You don’t always have to wait until the end to write your introduction. You should review it again of course, but since it's the setup [for the rest of your paper], it’s worth writing first.”
The introduction shows your reader what led to your research question. So, writing or outlining that part of the story early (and before you forget the details) can help provide accurate context.
3. Consider your introduction’s tone and tense
Use a formal, impersonal tone and speak primarily in the present tense. Double-check the tense used in each sentence or example since there’s a chance you’ll talk about past research in contrast with new processes. Avoid using emotional appeals as they are more suitable for conference presentations and public speaking.
FAQ: Top Abstract and Introduction Questions
Can I use my abstract as my introduction?
The short answer to this question: You shouldn’t. Unless the journal (or your research advisor) asks you to merge your abstract and introduction, it’s best to keep them unique.
Where can I find examples of abstracts and introductions?
This article by Kibin has 10 top-notch abstract examples to get you started. For a step-by-step guide to help you write an introduction, take a look at this article by Scribbr.
How do I write an abstract for an academic conference?
Conference abstract submission is unique. You may still be early in your research process and not have all the results yet. So, the things you include in your abstract will change. Check out our detailed article on writing an abstract for a conference to help you with this.
Apply What You Know About Abstracts and Introductions
Now that you know the key differences between an abstract and an introduction, it’s time to get started writing. If any points for your paper crossed your mind while reading this article, jot them down now to help with making your outline. And be sure to keep in mind: Your abstract is your advertisement. Your introduction is your hook.


